NOURIANZ® (istradefylline): A once-daily oral therapy
that patients can take when it fits their schedule
Dosing for NOURIANZ can be flexible—it can be taken any time, with or without food1
NOURIANZ has1:

- No food restrictions

- No time-of-day requirements
- No initial titration required
NOURIANZ comes in 2 dose strengths1:
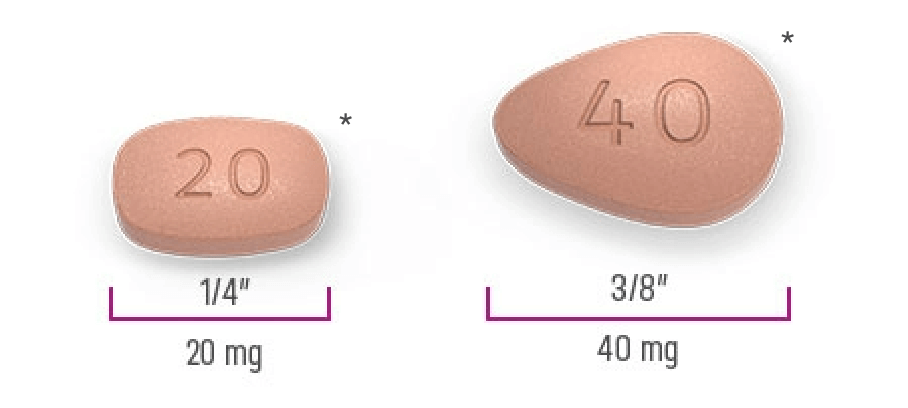
*Not actual size.
Recommended dosage adjustments for NOURIANZ1
- No dosage adjustments needed for mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment
- No dosage adjustment of levodopa/carbidopa is required when paired with NOURIANZ
| COADMINISTRATION OF NOURIANZ WITH: | DOSAGE RECOMMENDATIONS: |
|---|---|
| Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors | Maximum recommended dose of NOURIANZ is 20 mg/day |
| Strong CYP3A4 inducers | Avoid concomitant use |
| Tobacco smoking (≥20 cigarettes/day or equivalent of other tobacco product) | Recommended dose of NOURIANZ is 40 mg/day |
| ADMINISTRATION OF NOURIANZ IN PATIENTS WITH: | DOSING ADJUSTMENT/ RECOMMENDATION: |
|---|---|
| Mild hepatic impairment | No dosage adjustment needed |
| Moderate hepatic impairment | Maximum recommended dose of NOURIANZ is 20 mg/day |
| Severe hepatic impairment | Avoid concomitant use |
| Mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment | No dosage adjustment needed |
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
Dyskinesia: NOURIANZ in combination with levodopa may cause dyskinesia or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesia. In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with either NOURIANZ 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared to 0% for placebo.
Hallucinations / Psychotic Behavior: Because of the potential risk of exacerbating psychosis, patients with a major psychotic disorder should not be treated with NOURIANZ. Consider dosage reduction or discontinuation if a patient develops hallucinations or psychotic behaviors while taking NOURIANZ.
Impulse Control / Compulsive Behaviors: Patients treated with NOURIANZ and one or more medication(s) for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (including levodopa) may experience intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, intense urges to spend money, binge or compulsive eating, and/or other intense urges, and the inability to control these urges. In clinical trials, 1 patient treated with NOURIANZ 40 mg was reported to have impulse control disorder, compared to no patient on NOURIANZ 20 mg or placebo.
Drug Interactions
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily. Avoid use of NOURIANZ with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm.
Hepatic impairment: The maximum recommended dosage of NOURIANZ in patients with moderate hepatic impairment is 20 mg once daily. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions with an incidence ≥5% and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%) for NOURIANZ 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively.
Indication
NOURIANZ® (istradefylline) is an adenosine receptor antagonist indicated as adjunctive treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) experiencing “off” episodes.
You are encouraged to report suspected adverse reactions to Kyowa Kirin, Inc. at 1-844-768-3544 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see full Prescribing Information for NOURIANZ.
References: 1. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540. 2. Chen J-F, Cunha RA. The belated US FDA approval of the adenosine A2A receptor antagonist istradefylline for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Purinergic Signal. 2020;16(2):167-174. 3. Isaacson SH, Betté S, Pahwa R. Istradefylline for OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease: a US perspective of common clinical scenarios. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2022;12:97-109.
References: 1. Parkinson’s disease. National Institutes of Health. Updated June 26, 2023. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.nih.gov/research-training/accelerating-medicines-partnership-amp/parkinsons-disease 2. Olanow CW, Poewe W, Rascol O, Stocchi F. From OFF to ON—treating OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease. US Neurol. 2020;16(suppl 1):2-10.
References: 1. Kalia LV, Brotchie JM, Fox SH. Novel nondopaminergic targets for motor features of Parkinson's disease: review of recent trials. Mov Disord. 2013;28(2):131-144. 2. Mori A. Mode of action of adenosine A2A receptor antagonists as symptomatic treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:87-116. 3. Varani K, Vincenzi F, Tosi A, et al. A2A adenosine receptor overexpression and functionality, as well as TNF-α levels, correlate with motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2010;24(2):587-598. doi:10.1096/fj.09-141044. 4. Fuxe K, Marcellino D, Genedani S, Agnati L. Adenosine A2A receptors, dopamine D2 receptors and their interactions in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2007;22(14):1990-2017. doi: 10.1002/mds.21440. 5. Morelli M, Di Paolo T, Wardas J, Calon F, Xiao D, Schwarzschild MA. Role of adenosine A2A receptors in parkinsonian motor impairment and L-DOPA-induced motor complications. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;83(5):293-309. 6. Morelli M, Blandini F, Simola N, Hauser RA. A2A receptor antagonism and dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2012;2012:489853. doi: 10.1155/2012/489853. 7. Mishina M, Ishiwata K. Adenosine receptor PET imaging in human brain. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:51-69. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801022-8.00002-7. 8. The voice of the patient: Parkinson’s disease. Silver Spring, MD: US Food and Drug Administration; April 2016. https://www.fda.gov/media/124392/download. Accessed June 11, 2019. 9. Hickey P, Stacy M. Available and emerging treatments for Parkinson’s disease: a review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2011;5:241-254. 10. Stocchi F, Antonini A, Barone P, et al. Early DEtection of wEaring off in Parkinson disease: the DEEP study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014;20(2):204-211.
References: 1. Kulisevsky J, Poyurovsky M. Adenosine A2A-receptor antagonism and pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease and drug-induced movement disorders. Eur Neurol. 2012;67(1):4-11. 2. Mori A. Mode of action of adenosine A2A receptor antagonists as symptomatic treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:87-116. 3. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540. 4. DHIVY [package insert]. Alpharetta, GA: Avion Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021. 5. Morelli M, Blandini F, Simola N, Hauser RA. A2A receptor antagonism and dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2012;2012:489853. 6. Liu Y-J, Chen J, Li X, et al. Research progress on adenosine in central nervous system diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(9):899-910. 7. Mishina M, Ishiwata K. Adenosine receptor PET imaging in human brain. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:51-69. 8. Isaacson SH, Betté S, Pahwa R. Istradefylline for OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease: a US perspective of common clinical scenarios. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2022;12:97-109. 9. Chen J-F, Cunha RA. The belated US FDA approval of the adenosine A2A receptor antagonist istradefylline for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Purinergic Signal. 2020;16(2):167-174. 10. Brichta L, Greengard P, Flajolet M. Advances in the pharmacological treatment of Parkinson’s disease: targeting neurotransmitter systems. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36(9):543-554. 11. Kaakkola S, Wurtman RJ. Effects of COMT inhibitors on striatal dopamine metabolism: a microdialysis study. Brain Res.1992;587(2):241-249. 12. Kong P, Zhang B, Lei P, et al. Neuroprotection of MAO-B inhibitor and dopamine agonist in Parkinson disease. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):431-439. 13. Barrett MJ, Sargent L, Nawaz H, Weintraub D, Price ET, Willis AW. Antimuscarinic anticholinergic medications in Parkinson disease: to prescribe or deprescribe? Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2021;8(8):1181-1188. 14. Vanle B, Olcott W, Jimenez J, Bashmi L, Danovitch I, IsHak WW. NMDA antagonists for treating the non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):117. 15. Rascol O, Fabbri M, Poewe W. Amantadine in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20:1048-1056. 16. Rubí B, Maechler P. Minireview: new roles for peripheral dopamine on metabolic control and tumor growth: let’s seek the balance. Endocrinology. 2010;151(12):5570-5581. 17. Gerlach M, Double K, Arzberger T, Leblhuber F, Tatschner T, Riederer P. Dopamine receptor agonists in current clinical use: comparative dopamine receptor binding profiles defined in the human striatum. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2003;110(10):1119-1127. 18. Jenner P. Istradefylline, a novel adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;14(6):729-738. 19. Ishibashi K, Miura Y, Wagatsuma K, Toyohara J, Ishiwata K, Ishii K. Occupancy of adenosine A2A receptors by istradefylline in patients with Parkinson’s disease using 11C-preladenant PET. Neuropharmacology. 2018;143:106-112.
References: 1. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540. 2. Isaacson SH, Betté S, Pahwa R. Istradefylline for OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease: a US perspective of common clinical scenarios. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2022;12:97-109. 3. Mori A. Mode of action of adenosine A2A receptor antagonists as symptomatic treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:87-116. 4. Data on file. Kyowa Kirin Pharmaceutical Development, Inc., Princeton, NJ.
References: 1. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc. Princeton, NJ 08540. 2. Data on file. Kyowa Kirin Pharmaceutical Development, Inc., Princeton, NJ. 3. Wadhwa RR, Cascella M. Steady state concentration. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
References: 1. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc. Princeton, NJ 08540. 2. Data on file. Kyowa Kirin Pharmaceutical Development, Inc., Princeton, NJ. 3. Hauser RA, Hattori N, Fernandez H, et al. Efficacy of istradefylline, an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, as adjunctive therapy to levodopa in Parkinson’s disease: a pooled analysis of 8 phase 2b/3 trials. J Park Dis. 2021;11:1663-1675.
Reference: 1. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540.
References: 1. NOURIANZ [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin, Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540. 2. Isaacson SH, Betté S, Pahwa R. Istradefylline for OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease: a US perspective of common clinical scenarios. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2022;12:97-109. 3. Kulisevsky J, Poyurovsky M. Adenosine A2A-receptor antagonism and pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease and drug-induced movement disorders. Eur Neurol. 2012;67(1):4-11. 4. Mori A. Mode of action of adenosine A2A receptor antagonists as symptomatic treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:87-116. 5. DHIVY [package insert]. Alpharetta, GA: Avion Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2021. 6. Olanow CW, Poewe W, Rascol O, Stocchi F. From OFF to ON—treating OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease. US Neurol. 2020;16(suppl 1):2-10. 7. Chou KL, Stacy M, Simuni T, et al. The spectrum of “off” in Parkinson’s disease: what have we learned over 40 years? Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018;51:9-16.
Reference: 1. NOURIANZ. Prescribing Information. Kyowa Kirin, Inc; 2020. Accessed April 1, 2021. https://www.nourianzhcp.com/assets/pdf/nourianz-full-prescribing-information.pdf


 TOP
TOP